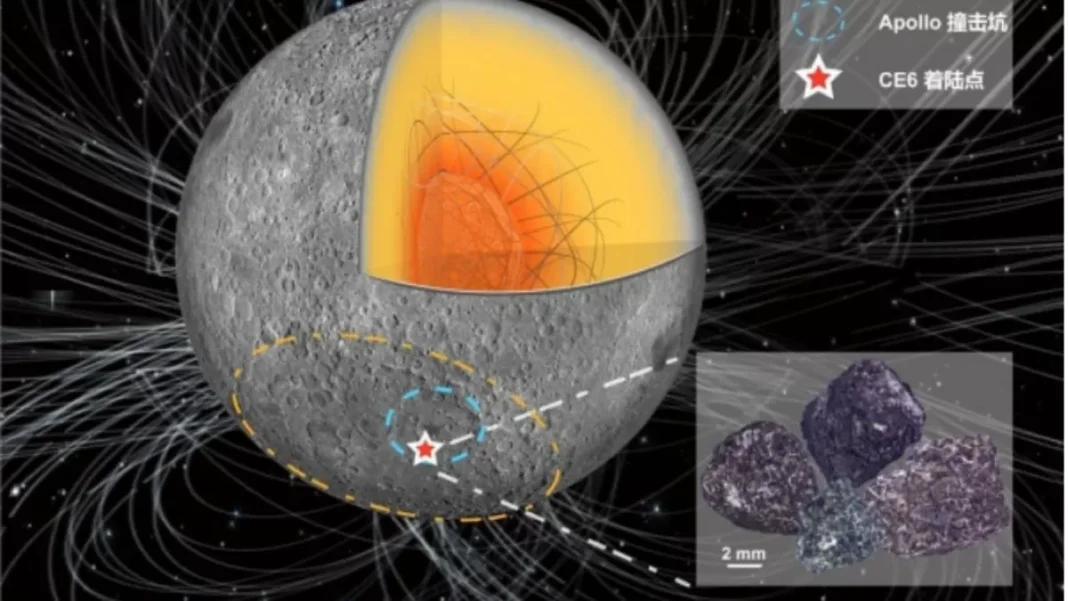
The Chang’e-6 mission, launched by China in 2023, has provided groundbreaking insights into the evolution of the lunar dynamo. The mission, which landed on the Moon’s surface in the South Pole-Aitken basin, has revealed a surprising magnetic field strength of 5 to 21 microteslas (µT) around 2.8 billion years ago. This discovery challenges previous assumptions that the lunar dynamo weakened after 3 billion years ago, and has opened up new possibilities for understanding the Moon’s magnetic field.
The lunar dynamo is a phenomenon that occurs when a planet or moon has a liquid metallic core that generates a magnetic field. This magnetic field is crucial for protecting the planet or moon from harmful solar radiation and cosmic rays. The Earth’s magnetic field, for example, is what shields us from the solar wind and allows life to thrive on our planet. However, the Moon’s magnetic field is much weaker, and scientists have been trying to understand why.
Previous studies have suggested that the lunar dynamo weakened and eventually disappeared around 3 billion years ago. This was thought to be due to the Moon’s small size and its cooling core. However, the Chang’e-6 mission has provided evidence that challenges this theory. The mission’s rover, equipped with a magnetometer, measured the magnetic field strength at different locations on the Moon’s surface. The surprising results showed that the magnetic field was much stronger than expected, even at a time when it was thought to have weakened.
The findings from the Chang’e-6 mission suggest that there may have been other mechanisms at play that maintained the lunar dynamo’s strength. One possible explanation is a basal magma ocean, which is a layer of molten rock that existed beneath the Moon’s surface. This magma ocean could have acted as a conductor, generating a strong magnetic field. Another theory is that the Moon’s core may have crystallized, creating a solid inner core that could have sustained the dynamo.
These new insights into the lunar dynamo’s evolution have significant implications for our understanding of the Moon’s history. It challenges the long-held belief that the Moon’s magnetic field weakened and disappeared early in its history. Instead, it suggests that the lunar dynamo may have been active for a longer period, and its strength may have fluctuated over time.
The Chang’e-6 mission’s findings also have implications for future lunar exploration. Understanding the Moon’s magnetic field is crucial for planning future missions and establishing a permanent human presence on the Moon. The magnetic field can affect spacecraft and astronauts, and knowing its strength and fluctuations is essential for their safety.
Moreover, the Chang’e-6 mission has once again demonstrated China’s capabilities in space exploration. The mission’s success is a testament to China’s technological advancements and its commitment to pushing the boundaries of scientific research. It also highlights China’s growing role in international space cooperation, as the mission’s data will be shared with other countries for further analysis.
The Chang’e-6 mission is part of China’s ambitious lunar exploration program, which aims to land humans on the Moon by 2030. The program has already achieved significant milestones, including the successful landing of the Chang’e-4 mission on the far side of the Moon in 2019. The Chang’e-6 mission’s findings will undoubtedly pave the way for future missions and contribute to our understanding of the Moon’s evolution.
In conclusion, the Chang’e-6 mission has provided crucial insights into the lunar dynamo’s evolution, challenging previous assumptions and opening up new possibilities for understanding the Moon’s magnetic field. The surprising magnetic field strength measured by the mission’s rover has shed light on the Moon’s history and has significant implications for future lunar exploration. This mission is a testament to China’s capabilities in space exploration and its commitment to advancing scientific knowledge for the benefit of all humanity.